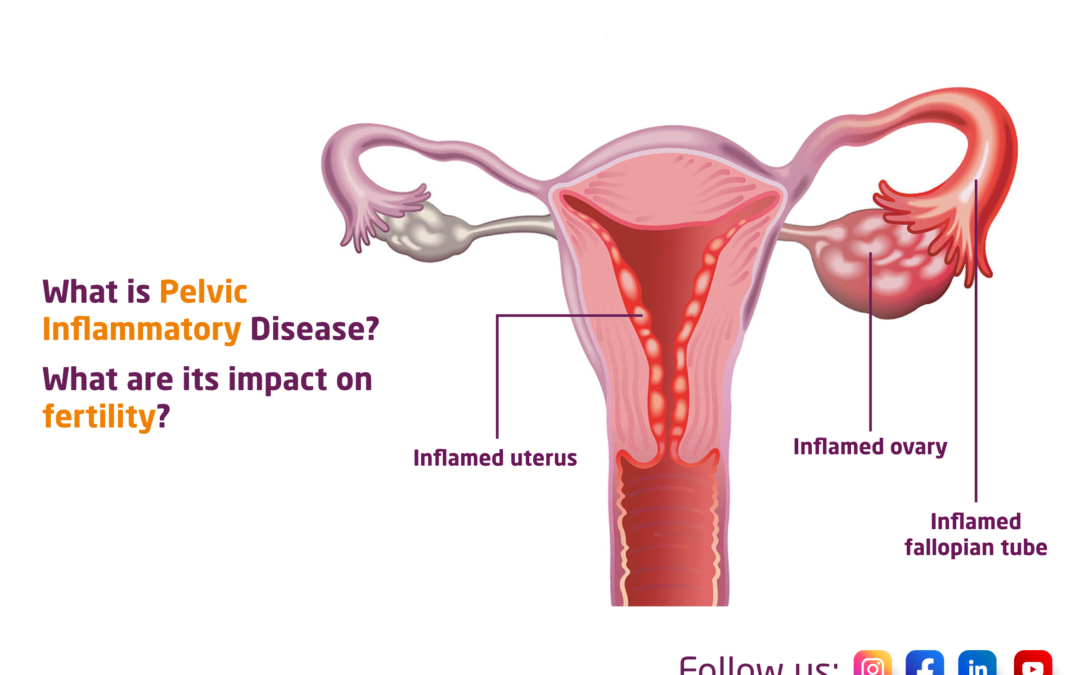
What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease? What are its impact on fertility?
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a severe infection that affects the reproductive organs of women. PID is caused by bacteria that enter the reproductive tract through the cervix and can cause inflammation and damage to the fallopian tubes, uterus, and ovaries. PID can have a significant impact on fertility, and in this blog post, we will explore what PID is and how it can affect a woman’s ability to conceive.
What is pelvic inflammatory disease?
Pelvic inflammatory disease is a bacterial infection that affects the reproductive organs of women. The bacteria that cause PID are usually sexually transmitted, including chlamydia and gonorrhoea. However, other types of bacteria can also cause PID, including those found in the vagina or cervix.
PID can cause inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes, which can prevent the egg from being fertilized and can also prevent the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus for implantation. If the infection is severe or goes untreated, it can lead to permanent damage to the reproductive organs, which can cause infertility.
What are the symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease?
The symptoms of PID can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis
- Pain during sex
- Painful urination
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
Some women may not experience any symptoms, but it is still essential to get tested if you think you may have been exposed to an STI or if you have any concerns about your reproductive health.
How does pelvic inflammatory disease impact fertility?
PID can impact fertility in several ways:
- Damage to the fallopian tubes: PID can cause inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes, which can prevent the egg from being fertilized and can also prevent the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus for implantation.
- Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy: If the fallopian tubes are damaged, the fertilized egg may implant in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus, which can cause an ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
- Chronic pain: Women with PID may experience chronic pelvic pain, which can affect their quality of life and make it more difficult to conceive.
- Increased risk of infertility: Severe or untreated PID can cause permanent damage to the reproductive organs, which can cause infertility.
How is pelvic inflammatory disease treated?
PID is usually treated with antibiotics to kill the bacteria that are causing the infection. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to administer intravenous antibiotics. It is important to treat PID as soon as possible to prevent further damage to the reproductive organs and to reduce the risk of complications.
Can PID be prevented?
PID can be prevented by practising safe sex, including using condoms and getting regular STI testing. If you suspect that you may have an STI, it is essential to get tested and treated as soon as possible to prevent the infection from spreading to the reproductive organs.
In addition to seeking medical attention and practising safe sex, there are a few other things you can do to help prevent PID and protect your reproductive health:
- Practice good hygiene: Keeping your genital area clean and dry can help prevent the growth of bacteria that can cause PID. Avoid using harsh soaps or douching, as this can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina and increase your risk of infection.
- Get vaccinated: The HPV vaccine can protect against certain types of HPV that can cause cervical cancer and other reproductive health issues, including PID. Talk to your doctor about whether the HPV vaccine is right for you.
- Stop smoking: Smoking can increase your risk of developing an STI and can also decrease your fertility. Quitting smoking can help protect your reproductive health and reduce your risk of developing PID.
If you do develop PID, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions for treatment and to attend all follow-up appointments. With prompt and effective treatment, most women with PID are able to recover fully and regain their fertility. However, in some cases, the damage to the reproductive organs may be permanent, making it more difficult or impossible to conceive naturally. If you are struggling with infertility after PID or have any concerns about your reproductive health, talk to your doctor about your options for fertility treatment.
In conclusion, pelvic inflammatory disease is a serious infection that can have a significant impact on fertility. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of PID or if you think you may have been exposed to an STI. By practising safe sex and getting regular STI testing, you can reduce your risk of developing PID and protect your reproductive health.