HSG Test
Make an Appointment
What is an HSG Test?
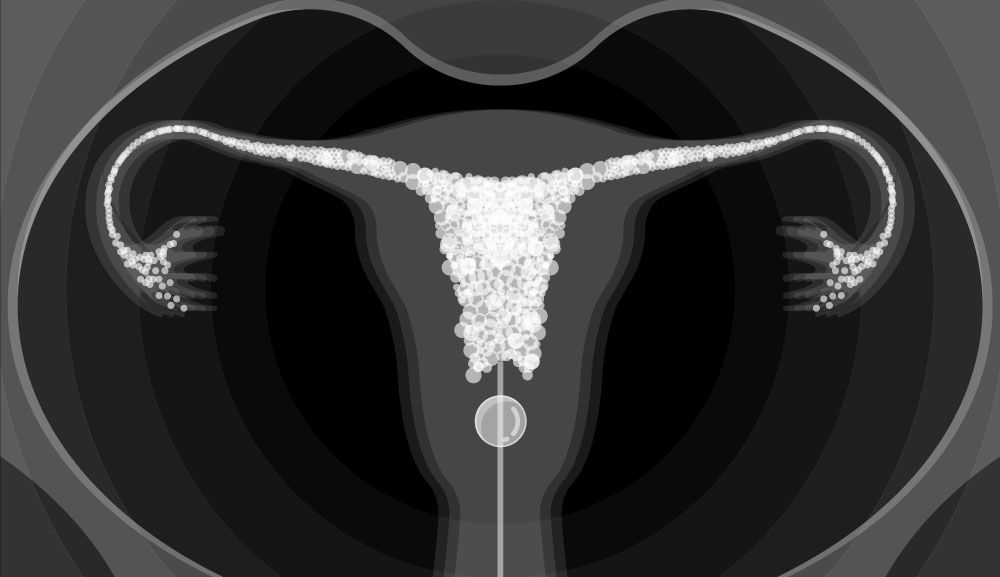
HSG, short for hysterosalpingography, is an imaging procedure that involves the injection of contrast dye into the uterus and fallopian tubes. X-ray images are then taken to visualize the structures and detect any abnormalities or blockages that may hinder pregnancy.
Procedure
a. Preparation: Prior to the HSG test, individuals may be advised to take over-the-counter pain medication to manage any potential discomfort. It is important to inform the doctor about any allergies, previous pelvic infections, or suspected pregnancy.
b. Administration of Contrast Dye: The procedure is typically performed in a radiology department. A speculum is inserted into the vagina, and a thin catheter is carefully placed through the cervix and into the uterus. Contrast dye is then slowly injected, allowing it to flow through the uterus and into the fallopian tubes.
c. X-ray Imaging: As the dye fills the reproductive structures, X-ray images are captured in real-time. These images provide valuable information about the shape and size of the uterus, any abnormalities, such as uterine fibroids or polyps, and the presence of blockages in the fallopian tubes.
d. Post-Procedure: After the HSG test, individuals may experience mild cramping or discomfort. Some providers recommend the use of antibiotics to prevent any potential infections. It is advisable to rest for the remainder of the day and avoid sexual intercourse for a short period, as advised by the doctor.
Importance of HSG in Infertility Evaluation
a. Evaluating Fallopian Tube Patency: The HSG test is primarily performed to assess the condition and patency of the fallopian tubes. Blockages or abnormalities in the tubes can prevent sperm from reaching the egg or hinder the transport of fertilized eggs to the uterus, leading to infertility.
b. Identifying Uterine Abnormalities: HSG can also detect uterine abnormalities that may affect fertility, such as uterine fibroids, polyps, adhesions, or structural anomalies. Identifying these issues helps guide appropriate treatment strategies.
Potential Benefits and Considerations
a. Treatment Guidance: The results of the HSG test can provide valuable information to doctors, enabling them to recommend appropriate fertility treatments. For example, if tubal blockages are detected, alternative methods like in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be suggested.
b. Psychological Considerations: The HSG test can have emotional implications for individuals and couples. It is important to have open communication with doctors and seek support to address any concerns or anxieties that may arise.
Risks and Limitations
HSG is generally considered safe, but there are potential risks, including allergic reactions to the contrast dye, pelvic infection (rare), or discomfort during the procedure. It is important to discuss any concerns with the doctor beforehand.
Conclusion
The HSG test is a valuable diagnostic procedure in the evaluation of infertility. Assessing the patency of the fallopian tubes and identifying uterine abnormalities, it provides essential information to guide fertility treatment decisions.
