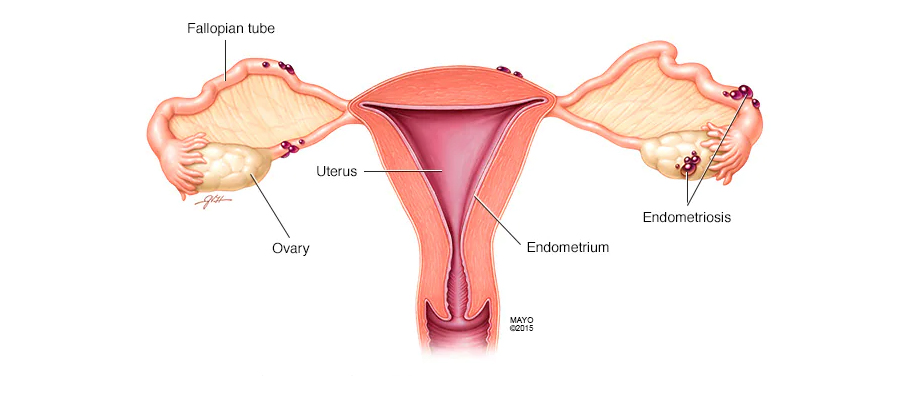
Endometriosis
Make an Appointment
Causes of Endometriosis
The exact cause of endometriosis is not yet fully understood. However, several theories exist. One of the most common theories is that during menstruation, some of the menstrual blood flows backwards through the fallopian tubes and into the pelvic cavity instead of out of the body. The endometrial cells that are present in the menstrual blood can then implant and grow in the pelvic area, leading to the development of endometriosis.
Another theory suggests that endometriosis may be caused by a problem with the immune system. This theory suggests that the immune system may not be able to recognize and destroy endometrial cells that have grown outside of the uterus.
Symptoms of Endometriosis
The symptoms of endometriosis can vary widely between women. Some women may have mild symptoms, while others may experience severe pain and other symptoms. Common symptoms of endometriosis include:
- Pelvic pain: This is the most common symptom of endometriosis. The pain may be severe and can occur during menstruation, intercourse, or bowel movements.
- Heavy periods: Women with endometriosis may experience heavy bleeding during their periods.
- Infertility: Endometriosis can affect fertility by causing scar tissue to form in the pelvic area, which can block the fallopian tubes or interfere with ovulation.
- Painful bowel movements: Women with endometriosis may experience pain during bowel movements.
- Fatigue: Endometriosis can cause fatigue and exhaustion.
Diagnosis of Endometriosis
The diagnosis of endometriosis can be difficult, as the symptoms can be similar to other conditions. The gold standard to diagnose endometriosis is through a laparoscopy, which is a surgical procedure that allows the doctor to view the inside of the pelvic cavity. During the procedure, the doctor will insert a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube with a camera) into the pelvic cavity to look for signs of endometriosis. A biopsy may also be taken to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of Endometriosis
There is currently no cure for endometriosis, but there are several treatment options available that can help manage the symptoms. Treatment options for endometriosis may include:
- Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain medication such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help manage the pain associated with endometriosis.
- Hormone therapy: Hormone therapy can help reduce the growth of endometrial tissue by suppressing ovulation. Hormone therapy may include birth control pills, progestin therapy, or GnRH agonists.
- Surgery: Surgery may be necessary to remove the endometrial tissue and scar tissue that has formed in the pelvic area. In severe cases, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be necessary.
- Fertility treatment: Women with endometriosis who are experiencing infertility may require fertility treatment, such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF), depending on the extent of endometriosis.
In conclusion, endometriosis is a chronic condition that can cause a range of symptoms, including pelvic pain, heavy periods, and infertility. If you are experiencing symptoms of endometriosis, it is important to talk to your doctor.
