DNA Fragmentation Testing
Make an Appointment
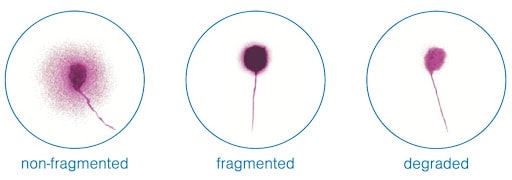
Understanding DNA Fragmentation
a. Sperm DNA Integrity: Sperm carry genetic material in the form of DNA, which is responsible for transmitting essential information to support fertilization and embryo development. DNA fragmentation refers to the occurrence of breaks or damage in the DNA strands of sperm, which can impair fertility potential.
b. Causes of DNA Fragmentation: Various factors contribute to DNA fragmentation, including oxidative stress, exposure to environmental toxins, infections, advanced paternal age, lifestyle choices (such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption), and certain medical conditions.
Significance of DNA Fragmentation Testing
a. Fertility Evaluation: DNA fragmentation testing provides valuable information about sperm quality and its impact on fertility. Traditional semen analysis may not identify issues related to DNA fragmentation, making this test an important addition to a comprehensive fertility evaluation.
b. Predictive Value: High levels of DNA fragmentation in sperm have been associated with reduced fertility, lower pregnancy rates, increased risk of miscarriage, and impaired embryo development. By assessing DNA fragmentation, potential reproductive challenges can be identified early, leading to more informed treatment decisions.
DNA Fragmentation Testing Methods
a. Comet Assay: The comet assay is a technique that assesses DNA integrity by measuring the migration of fragmented DNA strands. Sperm cells are embedded in a gel and subjected to an electric field, allowing damaged DNA to migrate away from the nucleus, forming a comet-like shape.
b. TUNEL Assay: The terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL) assay detects DNA breaks by labelling the ends of fragmented DNA strands with a fluorescent marker. The labelled DNA fragments can be visualized under a microscope, indicating the level of DNA fragmentation in sperm.
Interpreting DNA Fragmentation Results
a. Threshold Values: Different laboratories may have varying threshold values for determining normal or abnormal levels of DNA fragmentation. However, any value above 25% may indicate significant DNA damage.
b. Clinical Recommendations: A high level of DNA fragmentation may necessitate tailored treatment approaches, such as antioxidant therapy, lifestyle modifications, or advanced assisted reproductive techniques (e.g., intracytoplasmic sperm injection, ICSI) to maximize the chances of successful conception.
Future Perspectives:
a. Research and Advances: Ongoing research aims to further understand the impact of DNA fragmentation on fertility and refine testing methods to improve accuracy and clinical outcomes.
Conclusion
DNA fragmentation testing plays a crucial role in assessing sperm health and identifying potential causes of infertility. By evaluating the integrity of sperm DNA, this test provides valuable insights into reproductive challenges, helping doctors tailor treatment plans to maximize the chances of conception. As our understanding of DNA fragmentation continues to evolve, this diagnostic tool will play an increasingly important role in fertility evaluation, offering hope to individuals and couples seeking to build their families. Consulting with a fertility specialist and undergoing DNA fragmentation testing can provide personalized guidance and support on the journey towards achieving a successful pregnancy.
