Tesa_Pesa
Make an Appointment
Understanding TESA and PESA
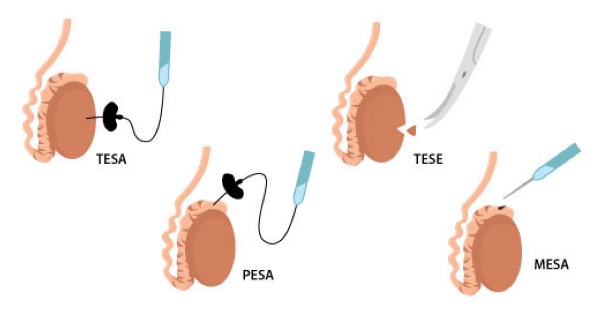
TESA (Testicular Sperm Aspiration): TESA is a minimally invasive procedure used to retrieve sperm directly from the testicles of men who have no sperm in their ejaculate. It is commonly performed in cases of obstructive azoospermia, where sperm production is normal, but there is a blockage preventing sperm from reaching the ejaculate. During TESA, a needle is inserted into the testicle, and sperm cells are aspirated, allowing for their subsequent use in assisted reproductive procedures like intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
PESA (Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration): PESA is a similar technique to TESA but involves the retrieval of sperm from the epididymis, a tubular structure located on the back of the testicle that stores and transports sperm. PESA is typically used in cases of non-obstructive azoospermia, where sperm production is impaired. During the procedure, a needle is inserted through the skin of the scrotum directly into the epididymis to aspirate sperm for use in assisted reproductive procedures.
Benefits of TESA and PESA
- Overcoming Male Infertility: TESA and PESA provide viable solutions for couples facing male infertility challenges. By directly retrieving sperm from the testicles or epididymis, these techniques bypass the barriers preventing sperm from reaching the ejaculate. This allows couples to pursue various assisted reproductive technologies such as IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) and ICSI, where the retrieved sperm can be used to fertilize eggs in the laboratory.
- Effective in Azoospermic Cases: Azoospermia, the absence of sperm in the ejaculate, can be caused by obstructive or non-obstructive factors. TESA and PESA cater to both types. TESA is particularly beneficial for men with obstructive azoospermia, where sperm production is normal, but there is a blockage in the reproductive tract. On the other hand, PESA is suitable for men with non-obstructive azoospermia, where sperm production is impaired. These procedures offer hope to individuals who might otherwise have limited options for biological parenthood.
- Minimally Invasive and Safe: TESA and PESA are considered minimally invasive procedures with a low risk of complications. They are typically performed under local anaesthesia and do not require major surgical incisions. The needle aspiration technique minimizes discomfort and reduces the recovery period, allowing individuals to resume their normal activities relatively quickly.
- Complementary to Assisted Reproductive Techniques: TESA and PESA are often combined with other assisted reproductive techniques, such as IVF or ICSI. The retrieved sperm can be used in conjunction with the partner’s eggs or donor eggs to facilitate fertilization and embryo development in the laboratory. This integrated approach maximizes the chances of achieving a successful pregnancy and ultimately becoming parents.
Conclusion
TESA and PESA are innovative assisted reproductive techniques that offer hope to couples grappling with male infertility. By directly retrieving sperm from the testicles (TESA) or epididymis (PESA), these procedures provide a solution for individuals with obstructive or non-obstructive azoospermia, where sperm is absent in the ejaculate. With their minimally invasive nature, TESA and PESA have become effective and safe options for retrieving sperm and enabling couples to pursue assisted reproductive technologies like IVF and ICSI.
