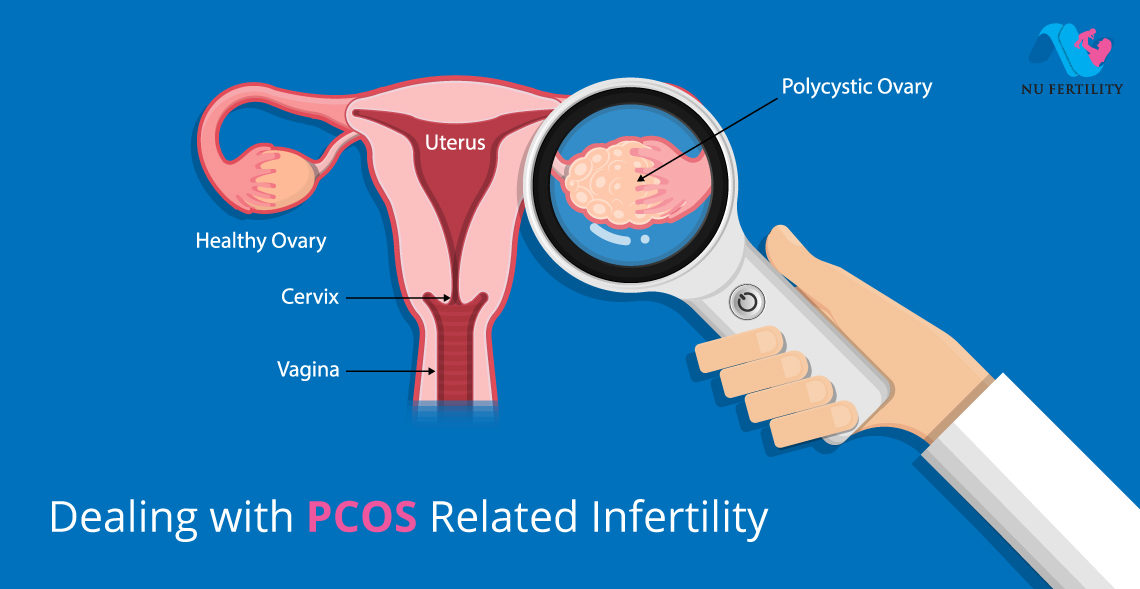
PCOS Treatment
Make an Appointment
Lifestyle Modifications:
a. Healthy Diet: A well-balanced diet, rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, can help manage PCOS symptoms. Avoiding processed foods, sugary snacks, and drinks with high glycemic index can regulate insulin levels and promote weight management.
b. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises, strength training, or yoga, can improve insulin sensitivity, aid in weight management, and alleviate PCOS symptoms.
c. Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in managing PCOS symptoms. Losing excess weight, if necessary, can regulate hormone levels, improve fertility, and reduce the risk of associated health complications.
Medications:
a. Oral Contraceptives: Birth control pills are often prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and alleviate symptoms like acne and hirsutism (excess hair growth).
b. Anti-Androgen Medications: These medications help block the effects of androgens and can improve symptoms like acne, hair loss, and excessive hair growth.
c. Insulin-Sensitizing Medications: Certain medications, such as metformin, can improve insulin resistance, regulate menstrual cycles, and assist with weight management in women with PCOS.
d. Fertility Medications: Women trying to conceive may be prescribed medications, such as clomiphene citrate or letrozole, to stimulate ovulation.
Assisted Reproductive Techniques:
a. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): In cases where PCOS-related infertility persists despite other treatments, IVF can be an option. It involves the retrieval of eggs, fertilization in a laboratory, and transfer of embryos into the uterus.
Other Supportive Therapies:
a. Ovulation Induction: For women with PCOS who desire pregnancy, ovulation induction may be recommended to stimulate regular ovulation. This can be achieved through medications like clomiphene citrate or gonadotropins.
b. Anti-Androgen Treatments: Additional therapies, such as laser hair removal or prescription creams, can be used to manage hirsutism and excessive hair growth.
Conclusion
PCOS is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted treatment approach. While there is no cure for PCOS, various treatment strategies can effectively manage its symptoms and promote overall health. Combining lifestyle modifications, medications, and supportive therapies tailored to individual needs can help regulate hormonal imbalances, improve menstrual regularity, enhance fertility, manage weight, and alleviate associated symptoms. If you suspect you have PCOS, it is crucial to consult with a fertility specialist to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific concerns and goals.
