Blastocyst Culture
Make an Appointment
Understanding Blastocyst Culture
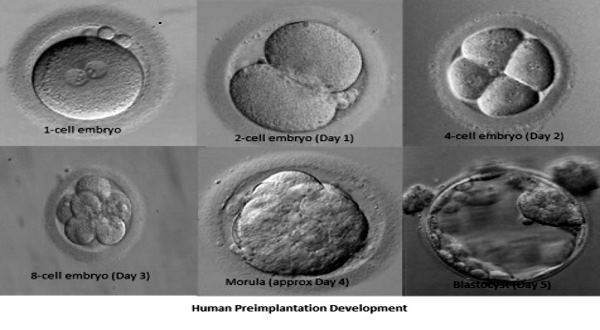
Blastocyst culture involves prolonging the in vitro development of embryos beyond the traditional three-day timeframe. Typically, embryos are transferred to the uterus on the third day after fertilization when they consist of six to eight cells. In contrast, blastocyst culture extends the development process to the fifth or sixth day, allowing the embryo to reach the blastocyst stage.
The blastocyst is a more advanced stage of embryonic development, characterized by two distinct components: the inner cell mass (ICM), which eventually forms the fetus, and the trophectoderm (TE), which develops into the placenta. By allowing embryos to reach the blastocyst stage, fertility specialists gain valuable insights into the quality and potential of the embryo, aiding in the selection of the most viable candidates for transfer.
The Benefits of Blastocyst Culture
- Improved Pregnancy Rates: One of the primary advantages of blastocyst culture is the ability to identify embryos with higher implantation potential. As embryos progress to the blastocyst stage, they undergo natural selection, where only the healthiest and most viable embryos continue to develop. Transferring these high-quality blastocysts into the uterus can significantly increase the chances of successful implantation and subsequent pregnancy.
- Enhanced Selection Process: Blastocyst culture provides fertility specialists with a more accurate means of assessing embryo quality. By monitoring the blastocyst’s morphology, cell count, and overall development, experts can identify embryos with a greater likelihood of implantation success. This improved selection process minimizes the risk of transferring embryos with chromosomal abnormalities or developmental issues, leading to higher pregnancy rates and healthier pregnancies.
- Reduced Risk of Multiple Pregnancies: Multiple pregnancies, such as twins or triplets, carry a higher risk of complications for both the mother and the babies. Blastocyst culture allows fertility specialists to identify and select the most robust embryos, reducing the need for multiple embryo transfers. By transferring a single high-quality blastocyst, the risk of multiple pregnancies can be significantly minimized, leading to safer outcomes for both mother and child.
- Time-Lapse Monitoring: Blastocyst culture often involves the use of time-lapse imaging systems, which capture images of the developing embryos at regular intervals. This allows fertility specialists to observe the embryo’s growth and behaviour over time, providing valuable information about the timing and pattern of cell division. Time-lapse monitoring can assist in identifying embryos with abnormal development or irregular cell divisions, enabling a better selection of embryos with the highest potential for a successful pregnancy.
Conclusion
Blastocyst culture represents a significant advancement in the field of assisted reproductive technologies. By extending the embryo development period and allowing embryos to reach the blastocyst stage, fertility specialists can select the most viable candidates for transfer, improving pregnancy rates while reducing the risk of multiple pregnancies. The ability to observe and assess embryos at a more advanced stage of development through time-lapse monitoring enhances the accuracy of the selection process. As technology continues to evolve, blastocyst culture offers promising prospects for couples undergoing fertility treatments, providing them with greater chances of successful pregnancies and healthier outcomes.
